
Remote Access VPN ensures that the connections between corporate networks and remote and mobile devices are secure and can be accessed virtually anywhere users are located. A secure remote access solution promotes collaboration by connecting global virtual teams at headquarters, branch offices, remote locations, or mobile users on the go. The VPN client was unable to successfully verify the IP forwarding table modifications. A VPN connection will not be established. Find the attached screen for mac os specification ipv6.
Best VPN service for Mac – private internet access for your online security
Get the best VPN connection for your online privacy and protection
Keep your personal information safe from identity thieves with VPN Client.
Protect your internet connection with VPN tunnel and get access to restricted internet content globally.
Get online, freedom, Security and Anonymity with Mac VPN Client
Unblock geo-located resources
Avoid identity thieves
Secure your internet connection while using public WiFi
View how websites appear at different locations
Why VPN Client Application?
Vpn Connection Client For Mac Os
VPN Server Locations
Our VPN servers are located in 60+ location over the world
- Fastest VPN speed and completely secure servers
- VPN unlimited bandwidth
- Select any of 90+ VPN servers
- A number of available servers are growing steadily
Australia
Brazil
Canada
Croatia
Spain
Finland
Germany
India
Israel
Japan
Sweden
Poland
Ukraine
Vpn Client For Mac
Table of contents
- 1.1. Initial configurations (only once at the first time)
- 2.2. Start a VPN connection
- 3.3. Enjoy VPN communication
Here is an instruction how to connect to a VPN Gate Public VPN Relay Server by using L2TP/IPsec VPN Client which is built-in on Mac OS X.
On this instruction, every screen-shots are taken on Mac OS X Mountain Lion. Other versions of Mac OS X are similar to be configured, however there might be minor different on UIs.
These screen-shots are in English version of Mac OS X. If you use other language, you can still configure it easily by referring the following instructions.
1. Initial configurations (only once at the first time)
Click the network icon on the top-right side on the Mac screen. Click 'Open Network Preferences...' in the menu.
Click the '+' button on the network configuration screen.
Select 'VPN' as 'Interface' , 'L2TP over IPsec' as 'VPN Type' and click the 'Create' button.
A new L2TP VPN configuration will be created, and the configuration screen will appear.
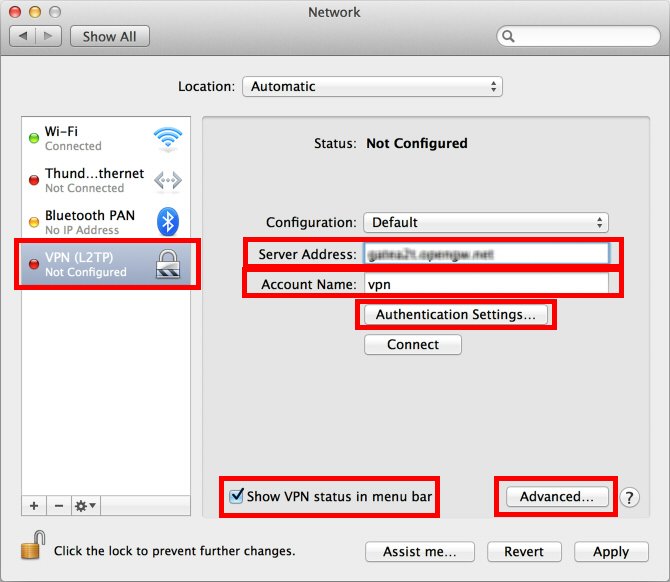
On this screen, you have to specify either hostname or IP address of the destination SoftEther VPN Server.
After you specified the 'Server Address' , input the user-name on the 'Account Name' field, which is the next to the 'Server Address' field.
Next, click the 'Authentication Settings...' button.
The authentication screen will appear. Input your password in the 'Password' field. Specify the pre-shared key also on the 'Shared Secret' field. After you input them, click the 'OK' button.
After return to the previous screen, check the 'Show VPN status in menu bar' and click the 'Advanced...' button.
The advanced settings will be appeared. Check the 'Send all traffic over VPN connection' and click the 'OK' button.
On the VPN connection settings screen, click the 'Connect' button to start the VPN connection.
2. Start a VPN connection
You can start a new VPN connection by clicking the 'Connect' button at any time. You can also initiate a VPN connection by clicking the VPN icon on the menu bar.
After the VPN connection will be established, the VPN connection setting screen will become as below as the 'Status' will be 'Connected' . Your private IP address on the VPN, and connect duration time will be displayed on the screen.
3. Enjoy VPN communication
While VPN is established, all communications will be relayed via the VPN Server. You can access to any local servers and workstation on the destination network.
